Know all about pulmonary embolisms
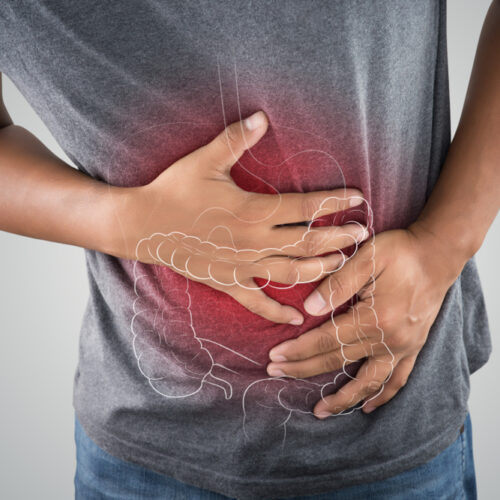
Pulmonary embolism is a condition which happens suddenly and is often life threatening if not attended to. It occurs when blood clots, most commonly, air bubbles lumps of fat from the marrow of long fractured bones or amniotic fluid. This blocks blood supply to areas that are provided by the artery and leads to the death of lung tissue.
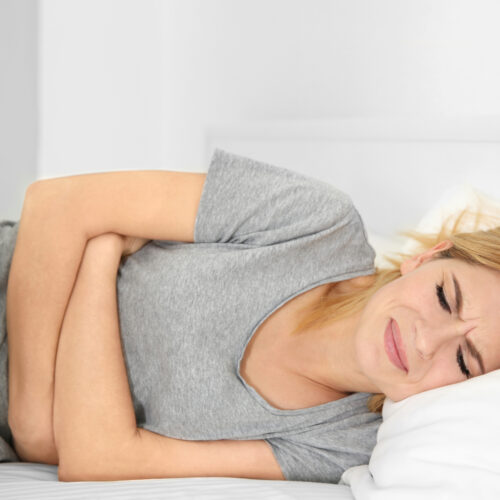
Blood clots are, generally migrated from legs where these are usually formed. Blood generally does not clot in the body. However, when the circulation becomes very slow and stagnant, they may get formed. There are other factors too that are involved. Pulmonary embolism generally presents the symptoms like shortness of breath and chest pain aggravated by exertion but not relieved by rest, bluishness of lips and skin, cyanosis, cough with blood or blood streaked sputum and dizziness. Other symptoms are rapid or irregular heart rate and copious sweating. In severe cases, the patient may lose consciousness or have a swollen and painful leg.
The general approach to treatment is to dissolve the clot and establish blood circulation. Towards this, anti coagulants like heparin are given. With some overlapping oral anti coagulants are also given. While these medicines would prevent further clot formation the body would dissolve the clot. Modern anti coagulants are fast acting and possibly avoid usage of heparin.
Standard body mechanisms will not allow blood to coagulate when in circulation. However, stagnating circulation especially in the legs and the condition of the lining of the veins and certain deficiencies in the blood would allow coagulation to happen. Long flights like, transatlantic in crowded seating arrangements should slow down the circulation the lower extremities to stagnation encouraging clot formation. Similarly, long bread rest as in certain fractures, heart attacks and major surgeries like knee replacements are other situations that promote coagulation of blood within the body.
It is important that general public is aware of symptoms and consequences of pulmonary embolism so that symptoms are recognized for what they are and getting medical attention in time to avoid a catastrophe.